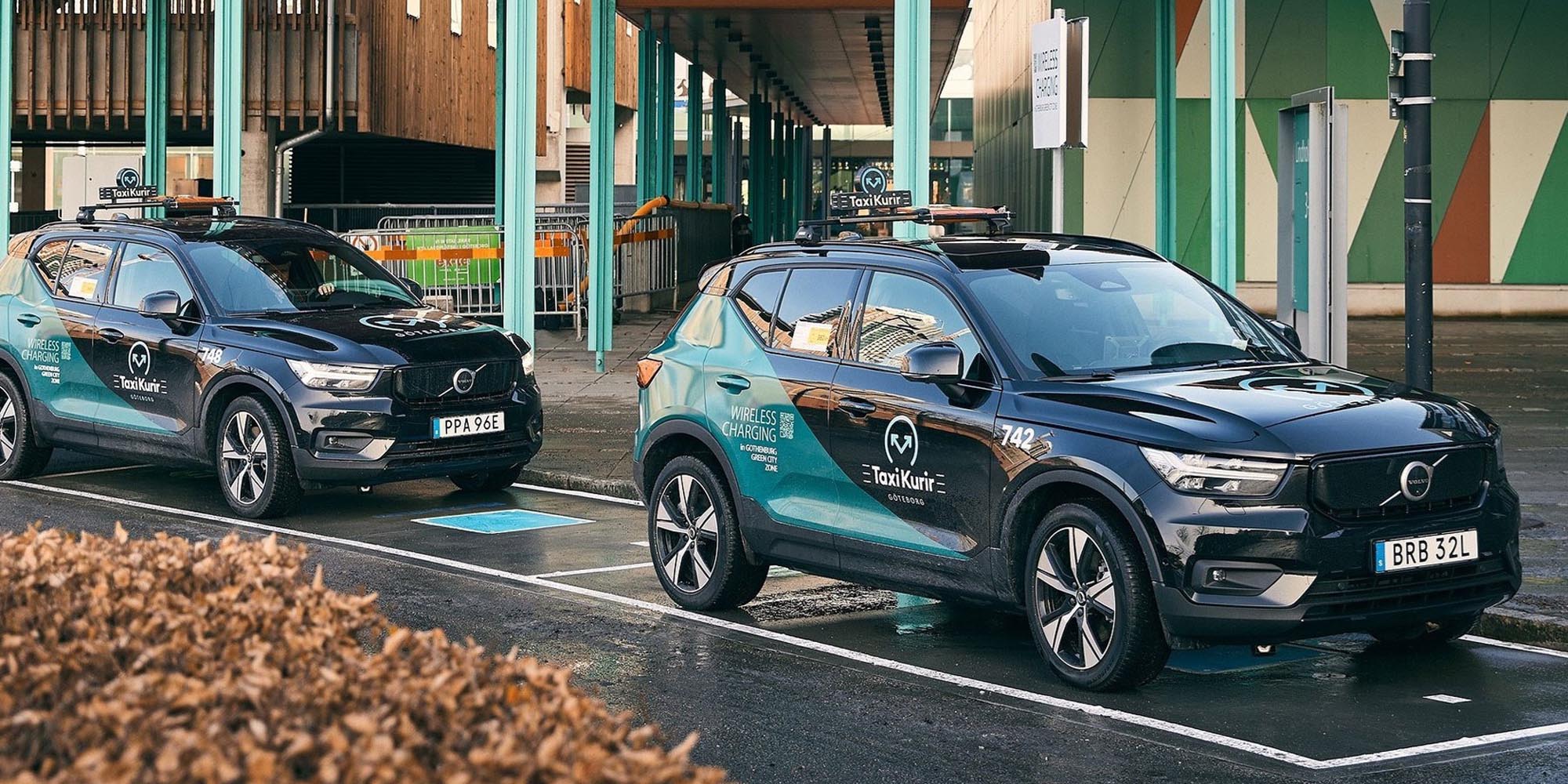
Introduction
As a revolutionary technology, wireless electric vehicle charging is transforming our understanding of traditional EV charging methods. This article will explore the current state and future prospects of wireless EV charging, helping you gain a comprehensive insight into this cutting-edge technology.
1.Basic Principles of Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging
1.1 What is Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging?
Wireless electric vehicle charging is an advanced technology that enables electric cars to charge without a physical connection, using electromagnetic induction or magnetic resonance techniques. In principle, it is similar to wireless charging for smartphones, but the technical requirements are higher and the application challenges greater.
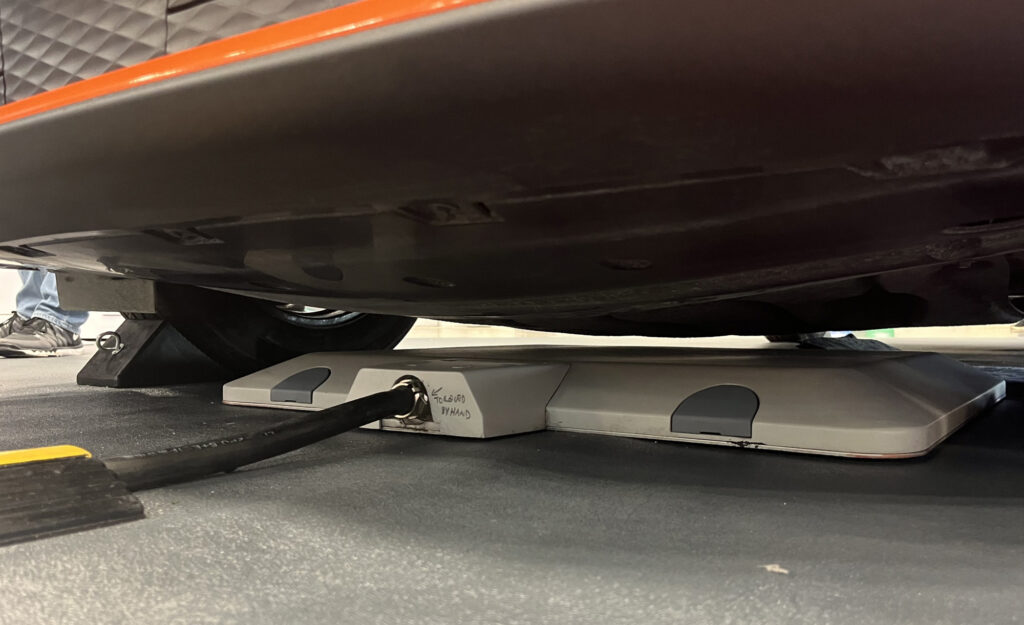

1.2 How Does Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging Work?
A wireless EV charging system primarily consists of two components: a ground transmitter and an onboard receiver. The ground transmitter is typically installed in parking spots or beneath roadways, while the onboard receiver is mounted on the underside of the electric vehicle. When the vehicle is parked in the charging zone, the ground transmitter uses an electromagnetic field to transfer electrical energy to the onboard receiver.
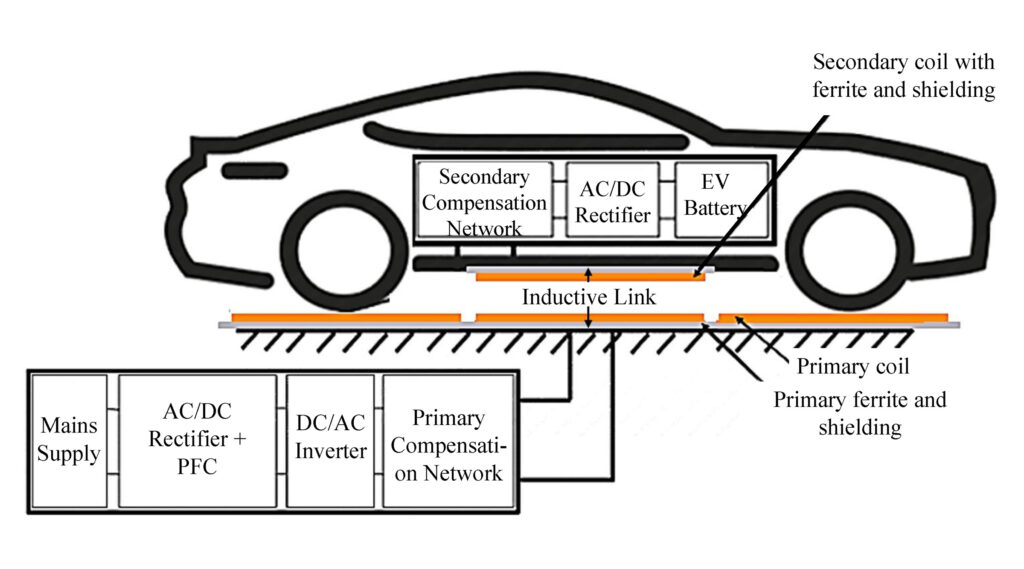
2.Current Status of Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging
2.1 Technical Status
Currently, wireless charging technology has made significant progress. Electromagnetic induction and magnetic resonance are the two main types of wireless charging methods. Electromagnetic induction technology is relatively mature and is widely applied in both residential and commercial charging scenarios. In contrast, magnetic resonance offers higher transmission efficiency and longer range but remains in the research and pilot stage.
2.2 Market Status
The market application of wireless charging technology is mainly focused on public transportation and commercial charging stations. For example, wireless bus charging systems have been implemented in several cities, significantly enhancing the operational efficiency of buses based on user feedback. Additionally, some high-end electric car brands are beginning to offer wireless charging services to improve the overall user experience.
2.3 Policy Support
Many countries and regions have begun to formulate policies that encourage and support the research and application of wireless charging technology. For instance, the European Union and the United States provide substantial funding for wireless charging R&D and pilot projects, while China is actively promoting the standardization and commercialization of wireless charging technology.
3.Challenges of Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging
3.1 Technical Challenges
Key technical challenges for wireless charging include transmission efficiency, safety, and cost. Transmission efficiency is central, as current wireless charging efficiency is slightly lower than that of wired charging. Additionally, electromagnetic interference and safety concerns remain critical issues to be resolved.
3.2 Market Challenges
Market acceptance of wireless charging technology is currently low due to high infrastructure costs and limited user awareness. The initial costs for wireless charging systems are high, and they require extensive infrastructure investments. Moreover, there is still a lack of broad user understanding of wireless charging technology.
3.3 Infrastructure Challenges
Developing wireless charging infrastructure demands significant investment and technical expertise. Government and industry cooperation is necessary to establish unified standards and planning to ensure compatibility and sustainability of the infrastructure. Furthermore, the maintenance and management of wireless charging infrastructure present additional challenges.
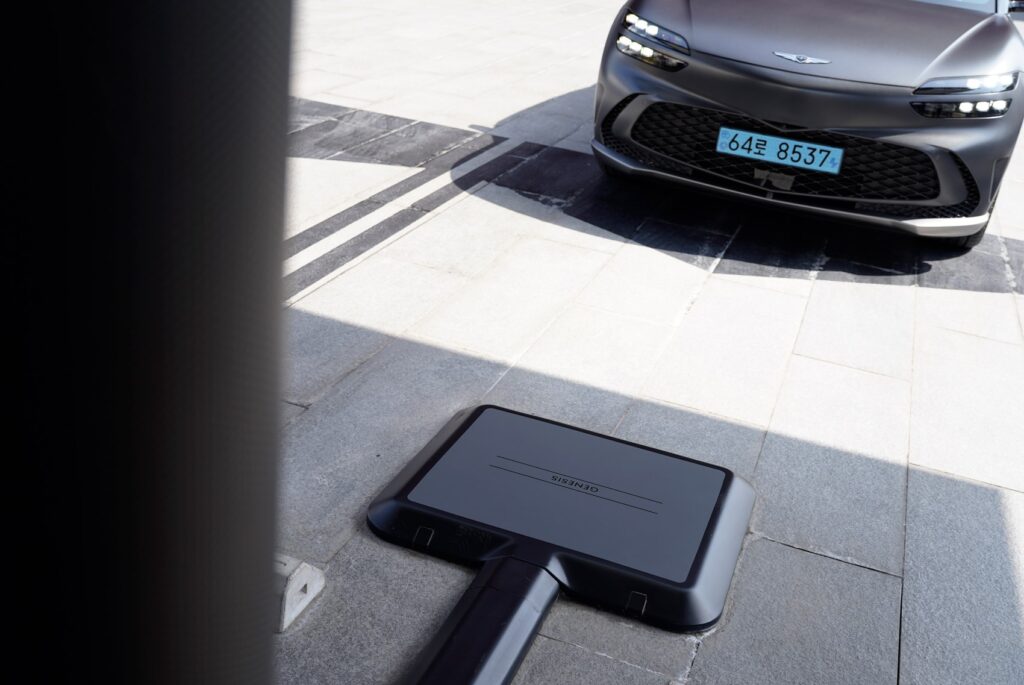

4.Future Prospects of Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging
4.1 Technological Advancements
With ongoing advancements in electromagnetic induction, magnetic resonance, and related technologies, wireless charging efficiency, transmission range, and safety are expected to improve further. In the foreseeable future, wireless charging technology may achieve higher power transmission and be applied in a broader range of scenarios.
4.2 Market Adoption
As technology continues to advance, costs decrease, and user awareness increases, wireless charging technology is expected to become the mainstream method for EV charging. It is anticipated that over the next decade, the wireless charging market will experience rapid growth, particularly in public transportation and commercial charging stations.
4.3 Policy Support
Government policy support and market promotion are key drivers for the widespread adoption of wireless charging technology. In the future, more countries and regions are expected to implement policies that encourage R&D and application of wireless charging, such as subsidies and tax incentives, which will help reduce system costs and stimulate innovation and market growth.
4.4 Standardization and Compatibility
For wireless charging technology to be widely adopted, standardization and safety are critical. Numerous companies and research institutions are currently working on developing standards for wireless charging to ensure that electric vehicles of various brands and models can use a unified system. As standards become more unified and compatibility increases, the application of wireless charging technology will expand further.
4.5 Dynamic Wireless Charging
Dynamic wireless charging technology enables electric vehicles to charge while in motion, which is particularly suitable for public transportation and long-distance travel. For example, wireless bus charging systems can charge buses during stops or even while driving, reducing waiting times and enhancing operational efficiency. In the future, dynamic wireless charging is expected to be widely adopted on highways and urban roads, significantly improving EV convenience and range.
4.6 Intelligent Charging Management
With the integration of the Internet of Things and artificial intelligence, wireless charging systems will achieve intelligent management. Intelligent charging management systems can optimize charging strategies based on grid load, user demand, and fluctuating electricity prices, thereby improving charging efficiency and user experience. For example, systems can automatically charge during off-peak hours to reduce costs.
4.7 Integration with Renewable Energy
Wireless charging systems can be combined with renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power to further reduce dependence on fossil fuels and enhance energy efficiency. In the future, wireless charging stations are expected to widely adopt renewable energy, achieve green charging, and reduce carbon emissions.
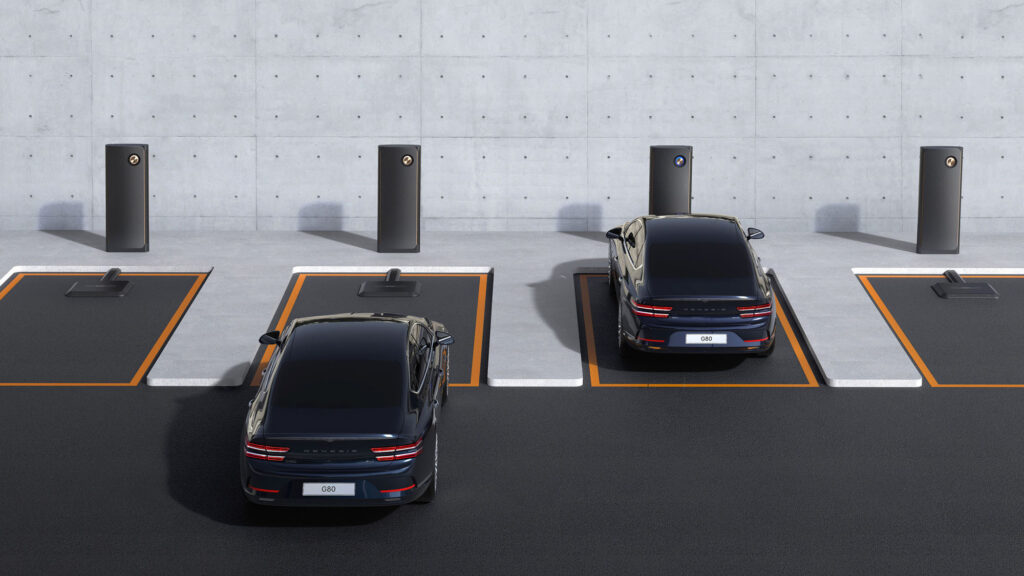

5.Global Applications of Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging
5.1 Europe
Europe is a leader in wireless charging technology, with several countries already conducting pilot projects. For instance, the UK and Germany have widely applied wireless charging technology in public transportation and commercial charging stations. London’s wireless bus charging system has been implemented, significantly enhancing bus operational efficiency.
5.2 United States
The United States is also at the forefront of wireless charging research and application. Numerous automobile manufacturers and technology companies are collaborating to promote the commercialization of wireless charging technology. For example, Tesla and BMW have introduced electric vehicles that support wireless charging.
5.3 Asia
In Asia, particularly in China and Japan, wireless charging technology is actively being promoted. China has invested heavily in electric vehicles and charging infrastructure, offering broad prospects for wireless charging technology. Japan’s R&D in wireless charging is also world-leading, with several companies having launched commercial wireless charging systems.
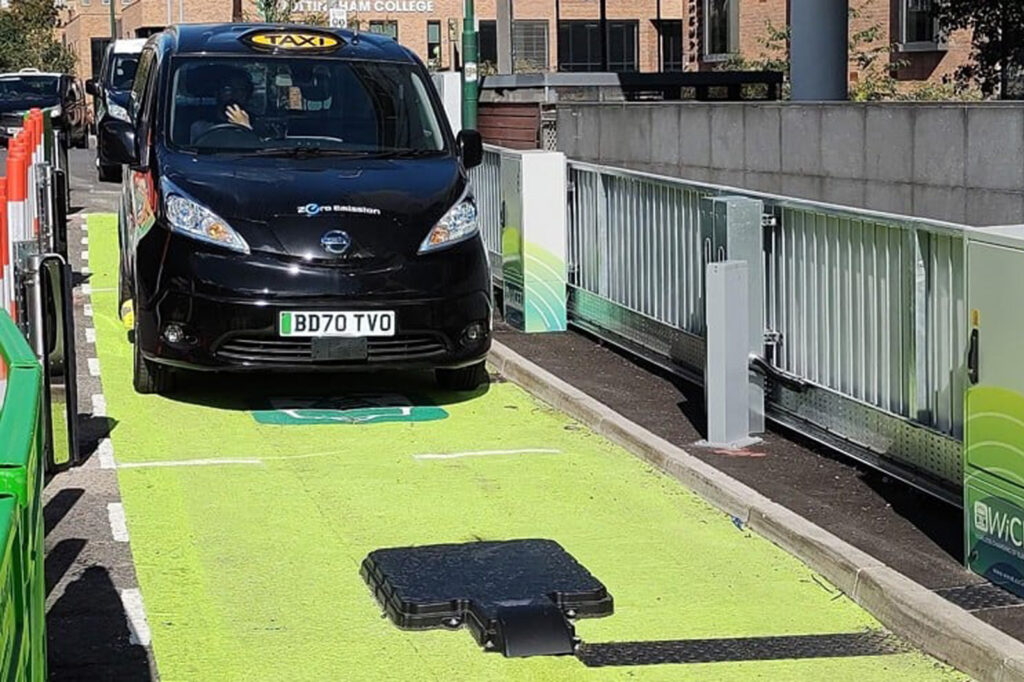

6.Environmental Benefits of Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging
6.1 Reduction of Carbon Emissions
Wireless charging technology can promote the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, reducing the use of traditional fuel vehicles, thereby lowering carbon emissions and mitigating climate change.
6.2 Promotion of Renewable Energy Use
Wireless charging systems can integrate with renewable energy sources like solar and wind, further decreasing reliance on fossil fuels and improving energy utilization efficiency.
6.3 Improvement of Urban Air Quality
The use of electric vehicles reduces exhaust emissions, contributing to improved urban air quality and enhancing the quality of life for residents.
Conclusion
As a revolutionary technology, wireless electric vehicle charging is transforming our current perception of EV charging. By gaining a thorough understanding of its working principles, efficiency, costs, and application scenarios, we can better grasp the future development trends of this technology. If you have any questions or require further information about wireless electric vehicle charging technology, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to providing you with professional services and support.

