Are you tired of waiting hours for your electric vehicle to charge? The slow charging times of EVs have been a significant barrier to widespread adoption, especially for long-distance travel.Level 3 charging, also known as DC fast charging (DCFC), offers a solution by significantly reducing charging times, potentially to mere minutes. It’s a crucial step towards alleviating range anxiety and boosting EV adoption.
But, is Level 3 charging truly a revolution, or is it an oversimplification? Let’s dive deeper and unravel the reality behind the buzzword.
Is Level 3 Charging Truly Revolutionary for EV Networks?
Is the slow charging of EVs a major drawback for your business operations? Level 3 promises to revolutionize the EV landscape, however, the biggest issue is charging time.
Level 3 charging isn’t a single, universally defined standard. It’s more of an umbrella term for DC fast charging (DCFC), which encompasses a wide range of power levels and connector types.

The “Level 3” Misconception
“Level 3” isn’t a rigidly defined standard. The term has evolved, and its meaning can shift. A “Level 3” charger might be a 50kW unit or a 350kW+ ultra-fast charger. The real breakthrough lies in DC fast charging, but even within DCFC, there’s a spectrum.
The Voltage Variable
Early “Level 3” chargers were around 400-500V. The real revolution is the move towards 800V and higher. This enables truly impressive charging speeds (e.g., 200 miles of range in under 20 minutes). However, this needs compatible vehicles, a major bottleneck.
| Feature | Level 2 Charging | Level 3 Charging (DCFC) |
| Voltage | 208-240V | 400-900V+ |
| Power | Up to 19.2 kW | 50kW – 350kW+ |
| Charging Time | Hours | Minutes |
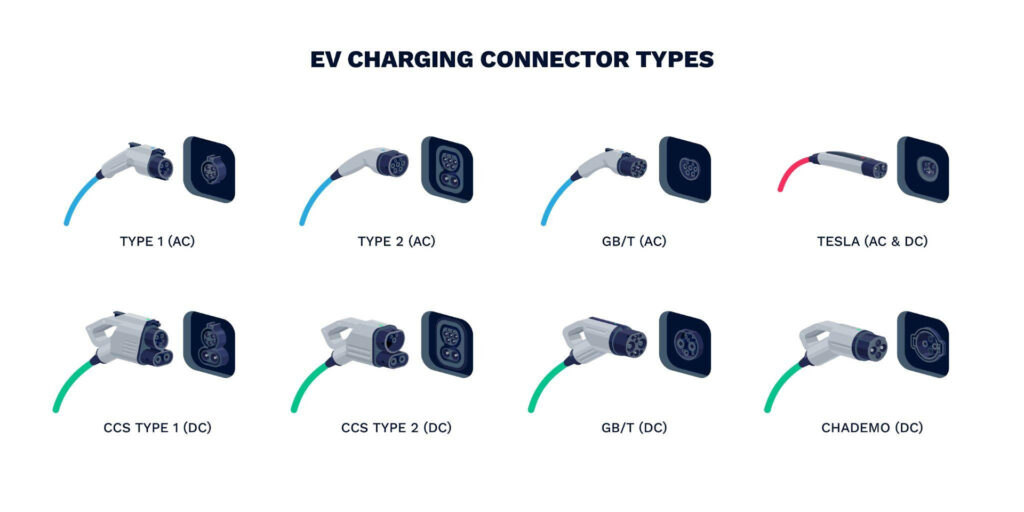
| Connector Types | J1772, Tesla | CCS, CHAdeMO, GB/T, Tesla |
What are the Unmatched Advantages of Level 3 Charging for Businesses?
Are slow charging times impacting your fleet’s efficiency or hindering your ability to attract EV-driving customers? Slow charging is a major problem for the commercial and public sectors.
Level 3 charging’s unmatched advantage is its speed. It can add significant range in a short amount of time (potentially hundreds of miles in under an hour), making it ideal for businesses that need quick turnaround times.

Advantages for Businesses
- Fleet Efficiency: Minimize downtime for electric delivery vehicles, taxis, or other commercial fleets.
- Customer Attraction: Attract and retain EV-driving customers by offering convenient, fast charging.
- Revenue Generation: Implement pay-per-use models or subscription services for charging.
- Brand Image: Demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and cutting-edge technology.
Beyond Speed: Other Benefits
- Compatibility: Most EVs with fast-charging capability can use Level 3 chargers, although connector types vary (CCS, CHAdeMO, GB/T).
- Promoting EV adoption: Fast charging reduces range anxiety.
What are the Technical Specifications and Standards for Level 3 Charging?
Confused by the different connector types and power levels? Don’t know which “Level 3” charger is right for you?
Level 3 chargers typically range from 50kW to 350kW (or even higher), with voltages ranging from 400V to 900V or above. Key standards include CCS, CHAdeMO, GB/T (China), and Tesla’s proprietary connector.
Technical Deep Dive
- Power Output: Measured in kilowatts (kW), this determines charging speed.
- Voltage: Higher voltage (800V+) enables faster charging but requires compatible vehicles.
- Connector Standards:
- CCS (Combined Charging System): Common in North America and Europe.
- CHAdeMO: Primarily used by Japanese automakers.
- GB/T: The standard in China.
- Tesla: Tesla uses its own proprietary connector, but adapters are available.
- Communication Protocols: Standards like OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) enable communication between the charger and the charging network.
Example Technical Parameter
| Model No. | Rated Power | Output Voltage | Input Voltage | Output Current |
| SDC20750 | 20kW | 150-750V | AC380V±20%(Optional) | DC:0~40A |
| VDC301K | 30kW | 150-750V | AC380V±20%(Optional) | DC:0~80A |
| HDC1201K | 120kW | 150-750V | AC380V±20%(Optional) | DC:0~200A |
What is the Real Cost of Level 3 Charging Infrastructure (Installation and Operation)?
Are you worried about the cost of implementing?
The real cost goes beyond the charger itself. It includes grid infrastructure upgrades, demand charges, installation, and ongoing maintenance, making detailed planning crucial.
The Hidden Costs
- Grid Infrastructure: A single 350kW charger can draw as much power as a small factory. Installing multiple high-power DCFCs often requires significant upgrades to the local grid.
- Demand Charges: Commercial electricity pricing includes peak demand charges. High-power DCFCs can trigger enormous demand charges.
- Installation: Costs vary depending on location, permits, and labor.
- Maintenance: These are complex systems requiring specialized technicians. Downtime is a major concern.
- Land Acquisition and Permitting:Finding suitable locations for charging stations needs near high-capacity power lines.
How Does Level 3 Charging Impact the Electrical Grid, and How Can We Mitigate It?
Worried about the impact of high-power charging on the electrical grid?
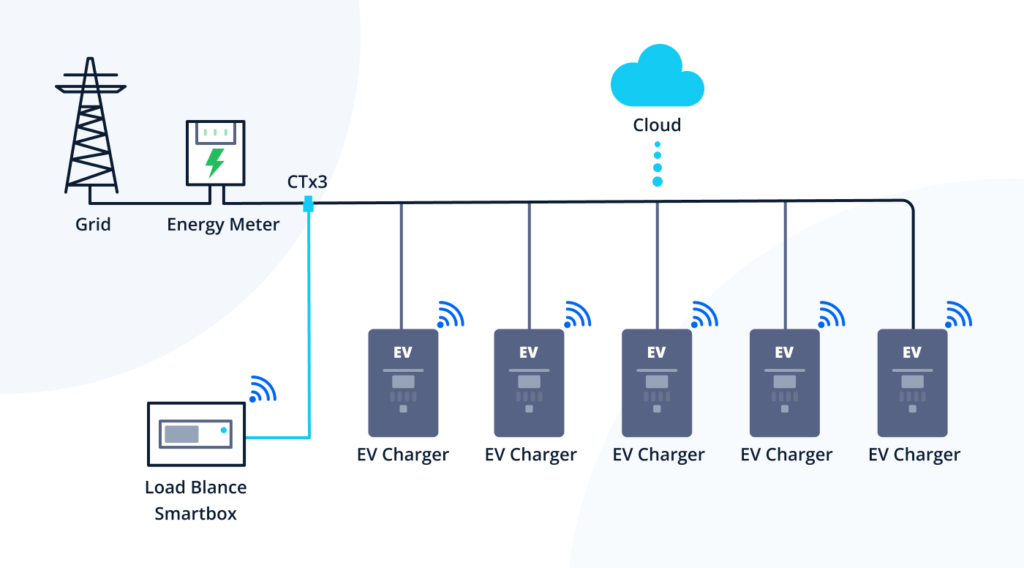
Level 3 charging can strain the grid, especially during peak demand periods. Mitigation strategies include smart charging, energy storage, and integration with renewable energy sources.
Grid Challenges and Solutions
- Peak Demand: High-power charging can create localized peaks in electricity demand, potentially overloading the grid.
- Mitigation Strategies:
- Smart Charging: Shift charging to off-peak hours.
- Energy Storage: Use batteries to store energy during low-demand periods and discharge it during peak demand.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Combine charging stations with solar or wind power.
- Dynamic Pricing: Implement pricing models that encourage charging during low-demand periods.
- V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) Technology: Allows EVs to send power back to the grid, helping to stabilize it.
What are the Key Use Cases and Deployment Strategies for Level 3 Charging?
Wondering where Level 3 charging makes the most sense?
Key use cases include highway corridors, urban fast-charging hubs, and commercial fleet depots. Strategic deployment is crucial for maximizing utilization and minimizing costs.

Ideal Use Cases
- Highway Corridors: Enable long-distance EV travel by providing fast charging along major routes.
- Urban Fast-Charging Hubs: Offer convenient, rapid charging in densely populated areas.
- Commercial Fleet Depots: Minimize downtime for electric delivery vehicles, taxis, or buses.
- Retail Locations: Attract EV-driving customers and generate revenue.
- Large Activity Venues: The product features fast deployment to meet the charging needs of a large number of electric vehicles during the event.
Deployment Considerations
- Site Selection: Proximity to high-capacity power lines, accessibility, and available space are key.
- Demand Forecasting: Estimate the number of EVs that will use the station and their charging patterns.
- Grid Capacity: Ensure the local grid can handle the added load.
- Partnerships: Collaborate with utilities, automakers, and other stakeholders.
- Future-Proofing: Consider future demand growth and technological advancements.
- Emergency Charging: Provide charging solutions in emergency.
What is the Future of Level 3 Charging and EV Charging Networks?
Wondering what’s next beyond Level 3?
The future involves even faster charging (e.g., Megawatt Charging System), wireless charging, battery swapping, and the integration of charging networks with smart grids and renewable energy.

Emerging Trends
- Megawatt Charging System (MCS): For heavy-duty vehicles, enabling charging at over 1 megawatt (1000 kW).
- Wireless Charging: Offers a more convenient and automated experience, especially for autonomous vehicles.
- Battery Swapping: Replacing a depleted battery with a fully charged one.
- Solid-State Batteries: Promise faster charging times and higher energy density.
- Extreme Fast Charging (XFC): XFC chargers are typically capable of delivering power at rates of 150 kW and higher, with some reaching 350 kW or more.
Is Level 3 the right solution for our charging needs?
Still unsure? I totally understand. It’s a big decision.
The correct answer is: it depends. Level 3 charging is ideal for situations requiring fast turnaround times, but a thorough assessment of your specific needs, budget, and site constraints is necessary. You need to consider whether you prioritize speed above all else.
As the founder of Jiangsu Tanxun New Energy Technology Co., Ltd., I’ve witnessed firsthand the evolution of EV charging technology. We’ve invested heavily in R&D to develop cutting-edge DC fast-charging solutions. Our customizable OEM/ODM services, including hardware, software, and communication protocols, are tailored to your specific needs. We operate six AC charging pile production lines and four DC charging pile lines, with an annual production capacity of 500,000 AC products and 10,000 DC products. We focus on green industrial practices and sustainable development, providing you with not only high-performance but also environmentally responsible solutions.
Factors to consider:
- Charging Speed Requirements: How quickly do you need to charge vehicles?
- Daily Usage Patterns: How many vehicles will be charging, and how often?
- Budget: What is your budget for infrastructure, installation, and ongoing operation?
- Available Power: Is your existing electrical infrastructure sufficient, or will upgrades be needed?
- Specific situation: Whether it is a family, a business, or an emergency situation.
Conclusion
Level 3 charging is a significant advancement, but understanding its complexities is vital. It’s not just about the charger; it’s about the entire ecosystem. Careful planning and strategic partnerships are critical for success.

