Are you struggling to decide between an electric vehicle (EV) and a traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle? It’s a big decision, with lots of factors to consider.The best choice depends on your individual needs, priorities, and driving habits. EVs generally excel in environmental impact and running costs, while ICE vehicles offer range and refueling convenience.
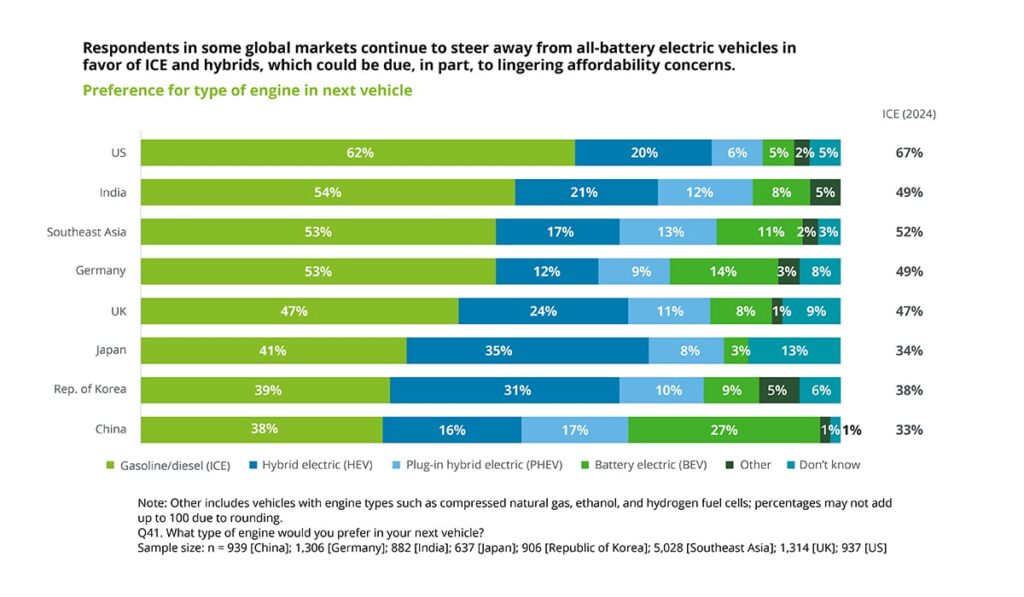
But let’s dive much deeper. I’ve spent years in the EV charging industry. This gives me unique insights to guide you through the process, breaking down every consideration for you.
Electric Vehicles vs. Fuel Vehicles: How Can Enterprise Fleets Make Informed Decisions?
Is your company wrestling with the decision to transition to an electric fleet? It’s a huge undertaking with complex implications.
Enterprise fleets should evaluate their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and sustainability goals. EVs can offer long-term cost savings and environmental benefits, but require careful planning for charging infrastructure and vehicle range.
Key Factors for Enterprise Fleets
For businesses, the decision goes beyond individual preferences. Here’s a structured approach:
- Route Analysis:
- Daily Mileage: Are your vehicles primarily used for short, predictable routes, or do they cover long, variable distances?
- Downtime: Do your vehicles have sufficient downtime for charging, or do they require quick turnaround times?
- Vehicle Type:
- Light-Duty Vehicles (Cars, Vans): EVs are increasingly viable for these applications.
- Heavy-Duty Vehicles (Trucks, Buses): EV technology is still developing for heavy-duty applications, but options are emerging.
- Financial Considerations:
- Incentives: Are there government incentives or tax breaks available for fleet electrification?
- Grants: Are there grants available to support the purchase of EVs and charging infrastructure?
| Feature | Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles |
| Decision Driver | Long-term cost savings, sustainability | Immediate operational needs, budget |
| Route Analysis | Short, predictable routes; ample downtime | Long, variable distances; quick turnaround |
| Vehicle Type | Light-duty vehicles | Heavy-duty vehicles (with caveats) |
| Finances | Incentives and grants may be available | Lower upfront purchase price |
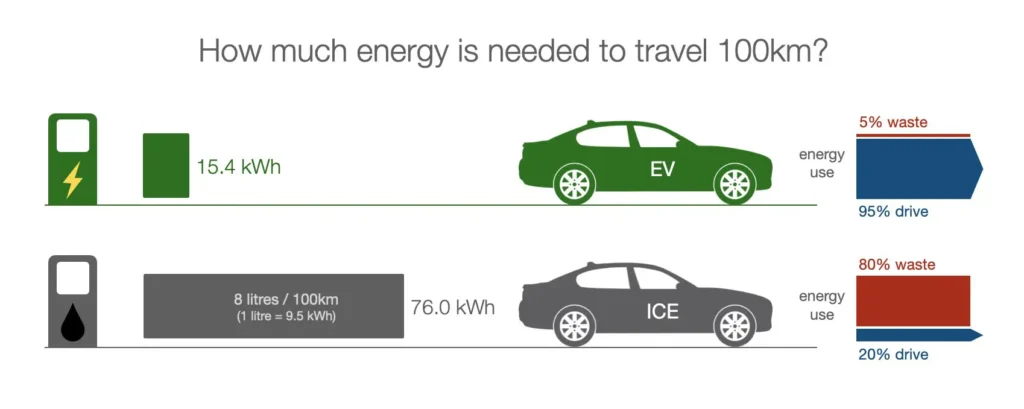
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Comparison: Are Electric Vehicles Really More Cost-Effective?
Is the upfront price of an EV scaring you away? Don’t let it!
While EVs often have a higher initial purchase price, their lower running costs (fuel and maintenance) can lead to a lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over the vehicle’s lifespan.
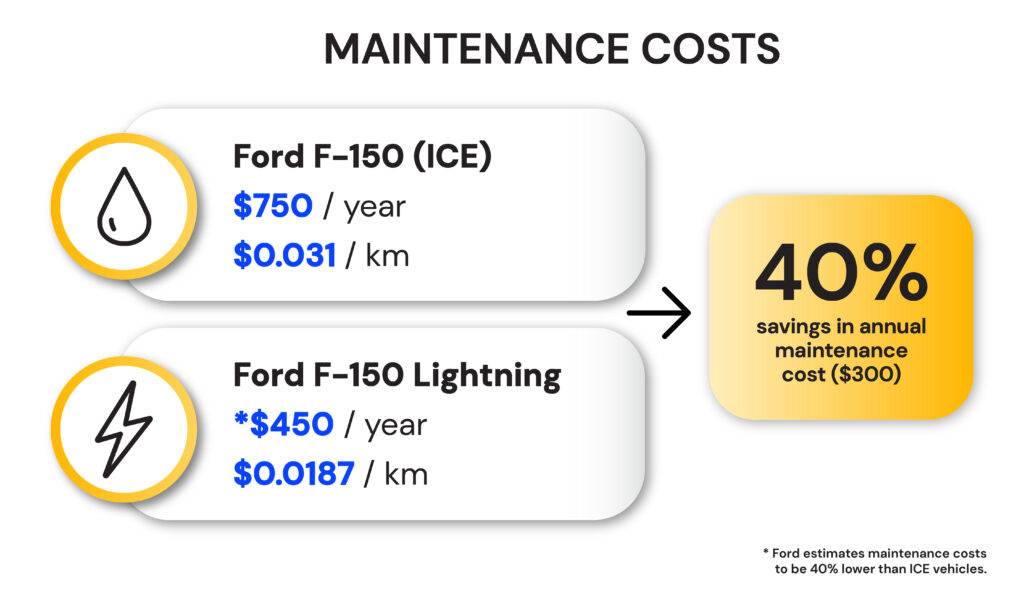
Breaking Down the TCO
Let’s dissect the components of TCO:
- Purchase Price: EVs typically have a higher sticker price, but government incentives can help offset this.
- “Fuel” Costs: Electricity is usually cheaper than gasoline or diesel. My experience shows significant savings, especially with home charging and time-of-use rates.
- Maintenance: EVs have far fewer moving parts, reducing maintenance needs. No oil changes, spark plugs, or complex exhaust systems!
- Depreciation: EVs have historically depreciated faster, but this is improving.
- Insurance:EV insurance can be more costly.
| Cost Component | Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles |
| Purchase | Higher (but incentives can help) | Lower |
| “Fuel” | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance | Lower | Higher |
| Depreciation | Historically higher, but improving | Lower |
| Insurance | May be Higher | Generally Lower |
Performance and Applicability: Can Electric Vehicles Meet Enterprise Operational Needs?
Worried about EVs not being powerful or reliable enough for your business? Think again.
EVs offer instant torque and smooth acceleration. While range was once a major limitation, it’s rapidly improving, with many models exceeding 200 miles on a single charge.
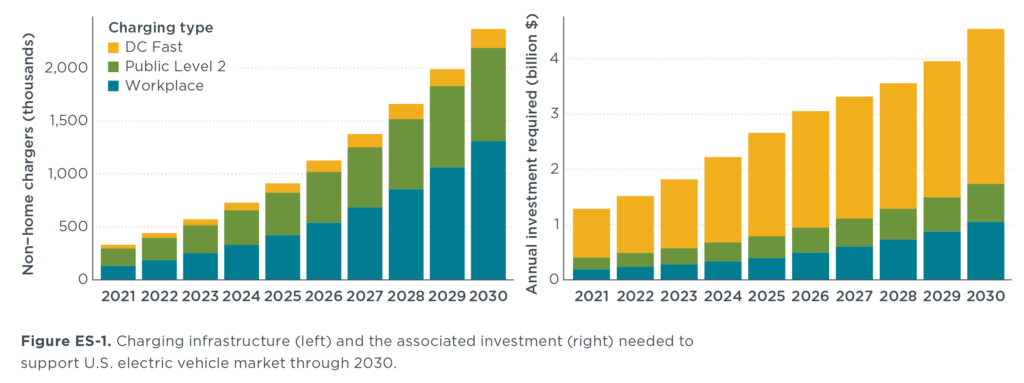
Addressing Operational Concerns
- Range Anxiety: The charging infrastructure is constantly expanding, and workplace charging can alleviate range concerns.
- Charging Time: DC fast charging can significantly reduce charging times, although it’s not always necessary for overnight charging.
- Payload Capacity: For heavy-duty applications, EV technology is still evolving, but options are becoming available.
- Durability: Modern EVs are built to withstand rigorous use.
| Operational Concern | Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles |
| Range | Improving rapidly; many models exceed 200 miles | Longer range on a full tank |
| Charging Time | Varies; DC fast charging can be quick, overnight charging slower | Refueling is quick |
| Payload | Evolving for heavy-duty; sufficient for light-duty | Generally higher payload capacity for heavy-duty |
| Durability | Built to withstand rigorous use, batteries can last up to 12-15 years | Varies depending on make/model. |
Environmental Impact and Corporate Social Responsibility: How Can Electric Vehicles Contribute to Sustainability?
Do you want to make your business greener? This is where EVs really shine.
EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing air pollution, especially in urban areas. This is a major step toward corporate social responsibility and sustainability goals.
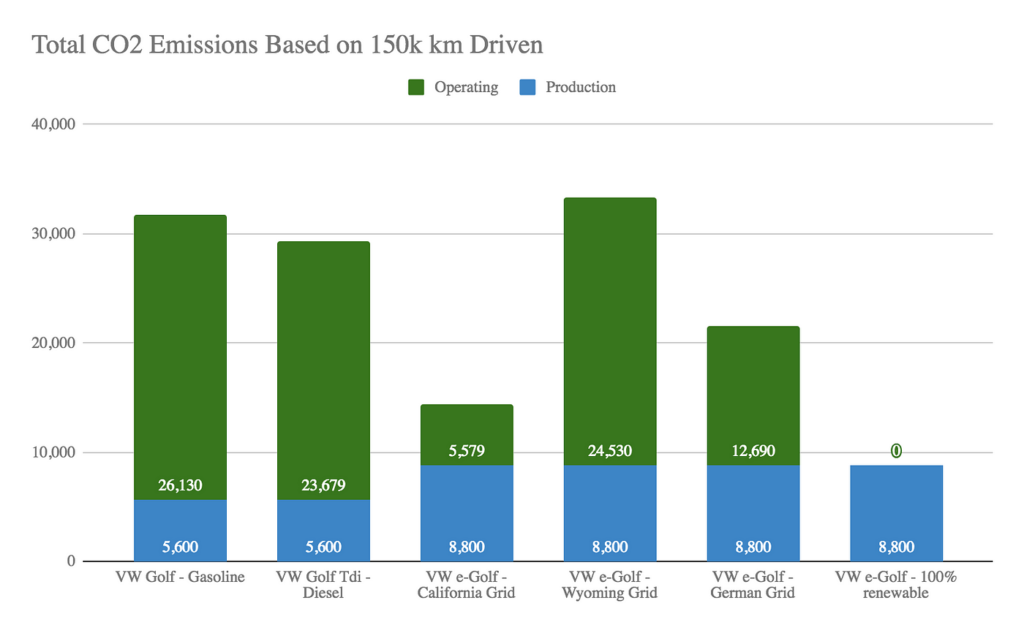
The Bigger Environmental Picture
- Lifecycle Emissions: Even considering the emissions from electricity generation, EVs generally have a lower carbon footprint than ICE vehicles, especially when using renewable energy sources.
- Air Quality: Zero tailpipe emissions mean cleaner air, leading to improved public health.
- Resource Depletion: EVs reduce reliance on fossil fuels, a finite resource.
- Noise Pollution: EVs are Much quieter.
| Environmental Factor | Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles |
| Tailpipe Emissions | Zero | Significant |
| Lifecycle Emissions | Generally lower | Higher |
| Air Quality | Improves air quality | Contributes to air pollution |
| Resource Use | Reduces reliance on fossil fuels | Relies on fossil fuels |
Infrastructure Support: How to Prepare for Electric Vehicle Fleets?
Thinking the switch to EVs sounds like an infrastructure nightmare? It doesn’t have to be.
Preparing for an EV fleet requires careful planning for charging infrastructure. This may involve installing on-site chargers, utilizing public charging networks, or a combination of both.
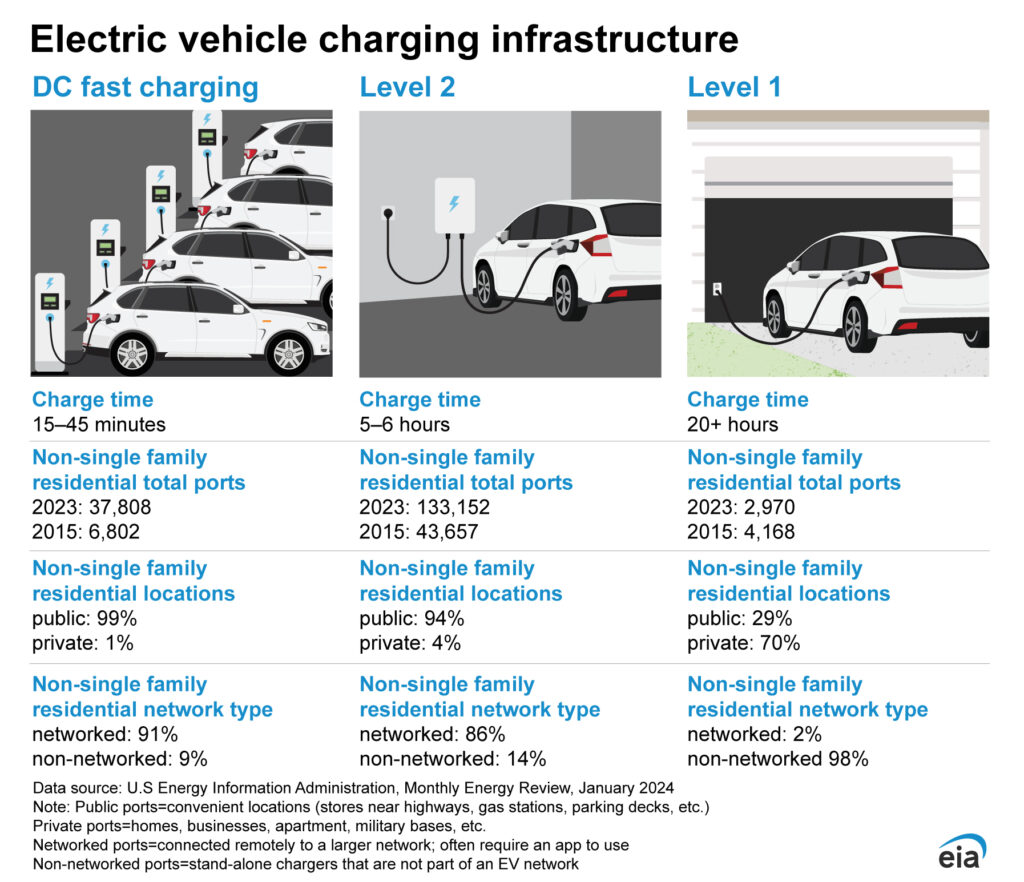
Charging Solutions
- Level 2 Charging: This is the most common type of charging for workplaces and homes, providing a full charge overnight.
- DC Fast Charging: This provides a rapid charge, often 80% in under an hour, suitable for quick top-ups.
- Workplace Charging: Installing chargers at your business location provides convenient charging for employees and fleet vehicles.
- Public Charging Networks: These are expanding rapidly, offering additional charging options.
- Charging Management Software: Smart Charging, Load Balancing.
| Charging Solution | Description | Use Case |
| Level 2 Charging | Most common type; provides a full charge overnight (typically 20-25 miles of range per hour of charging). | Workplace charging, home charging |
| DC Fast Charging | Rapid charging; often 80% in under an hour. | Quick top-ups, long-distance travel |
| Workplace Charging | Chargers installed at the business location. | Convenient charging for employees and fleet vehicles |
| Public Charging | Expanding network of publicly available chargers. | Additional charging options, especially for drivers without home charging |
Future Trends: How Will Electric Vehicle Technology and Markets Develop?
Wondering if EVs are just a passing fad? Absolutely not!
EV technology is advancing rapidly, with improvements in battery range, charging speed, and cost. Government policies are increasingly supporting EV adoption, driving market growth.
What to Expect
- Battery Technology: Expect longer ranges, faster charging times, and lower battery costs in the coming years. Solid-state batteries are a promising development.
- Charging Infrastructure: The charging network will continue to expand, with more public and private charging options becoming available.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology: This will allow EVs to send energy back to the grid, providing grid stability and potentially generating revenue for EV owners.
- Autonomous Driving: EVs are well-suited for autonomous driving technology, and the two are likely to develop in tandem.
- Government Policy:Increasing support EV.
| Future Trend | Description | Impact |
| Battery Technology | Longer ranges, faster charging, lower costs; solid-state batteries. | Increased EV adoption, reduced range anxiety |
| Charging Infrastructure | Expanding network of public and private chargers. | Greater convenience, reduced reliance on home charging |
| V2G Technology | EVs can send energy back to the grid. | Grid stability, potential revenue for EV owners |
| Autonomous Driving | EVs and autonomous driving are developing together. | Potential for increased safety, efficiency, and new mobility services |
Conclusion
Making a choice between an electric vehicle and an internal combustion engine vehicle is a complex decision that has long-term implications. As one of China’s top manufacturers of EV charging products, TX’s high-quality services can assist you in making the best choice. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us at any time.