In today’s era, electric vehicles (EVs) have gradually become a daily transportation choice for many due to their environmental and energy-saving features. But have you ever wondered how these quiet and efficient vehicles made their way into our lives? Let’s travel through time and explore the legendary history of electric vehicles.
Early Exploration: The Birth of Electric Vehicles
In 1834, American Thomas Davenport created the first practical electric vehicle powered by a DC motor. Although its speed and range were extremely limited, this invention marked the beginning of the electric vehicle era, like the first light in the darkness, pointing the way forward for future development.
In 1873, British inventor Robert Davidson built a more advanced electric vehicle that used rechargeable lead-acid batteries, improving its performance. Despite being inferior to steam and later gasoline-powered cars in terms of speed and range, early electric vehicles attracted attention due to their quiet operation, lack of fumes, and ease of use, laying the foundation for the modern electric vehicle industry.

First Golden Age: The Rise of Electric Vehicles
From the late 19th to the early 20th century, electric vehicles entered their first golden age. During this period, significant advancements were made in EV technology. Improvements in battery technology increased the range of electric vehicles, and manufacturing processes became more refined.
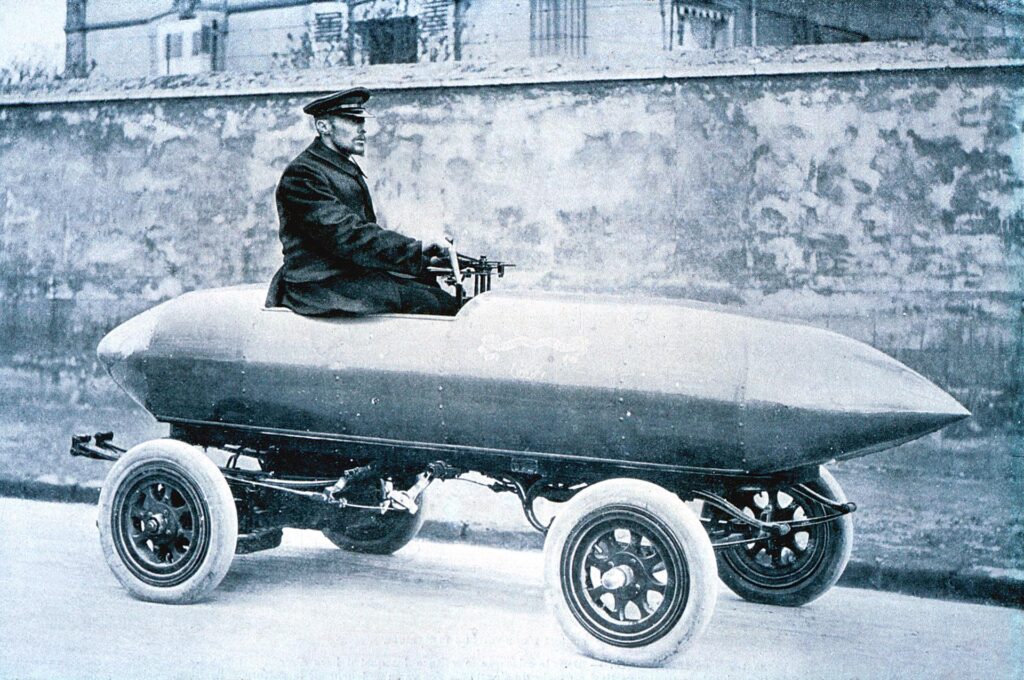
In 1899, Belgian engineer Camille Jenatzy drove an electric car named “La Jamais Contente” to a record speed of 105.88 km/h, astonishing the world and showcasing the potential of electric vehicles.
During this time, electric vehicles also achieved some market success. In 1900, electric vehicles accounted for about one-third of car sales in the United States. In urban areas, EVs were favored for their noiseless operation and ease of use, especially among female drivers. Electric vehicles became a symbol of fashion and status, with many wealthy individuals and celebrities owning their own EVs.
The Rise of Gasoline Cars: The Decline of Electric Vehicles
However, with the rapid development of the oil industry, gasoline-powered cars also advanced quickly. In 1886, German inventor Karl Benz created the first gasoline-powered car, marking the beginning of the gasoline car era. Gasoline cars had clear advantages in range and refueling speed, and as mass production increased, their costs decreased, allowing them to capture more market share.
In contrast, electric vehicles faced numerous bottlenecks. Battery technology stagnated, limiting the range and charging times of EVs. Additionally, the lack of infrastructure made it difficult to promote electric vehicles effectively. By the 1930s, electric vehicles had almost disappeared from the market, entering a long period of decline.
Technological Breakthroughs: The Dawn of Revival
In the 1960s, as environmental issues and oil crises emerged, people began to reconsider the value of electric vehicles. Governments and companies increased investment in EV technology, leading to a series of breakthroughs that brought hope for the revival of electric vehicles.
In terms of battery technology, the emergence of nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries significantly improved the performance of electric vehicles. Advances in motor control systems and lightweight materials also enhanced the efficiency and range of EVs.
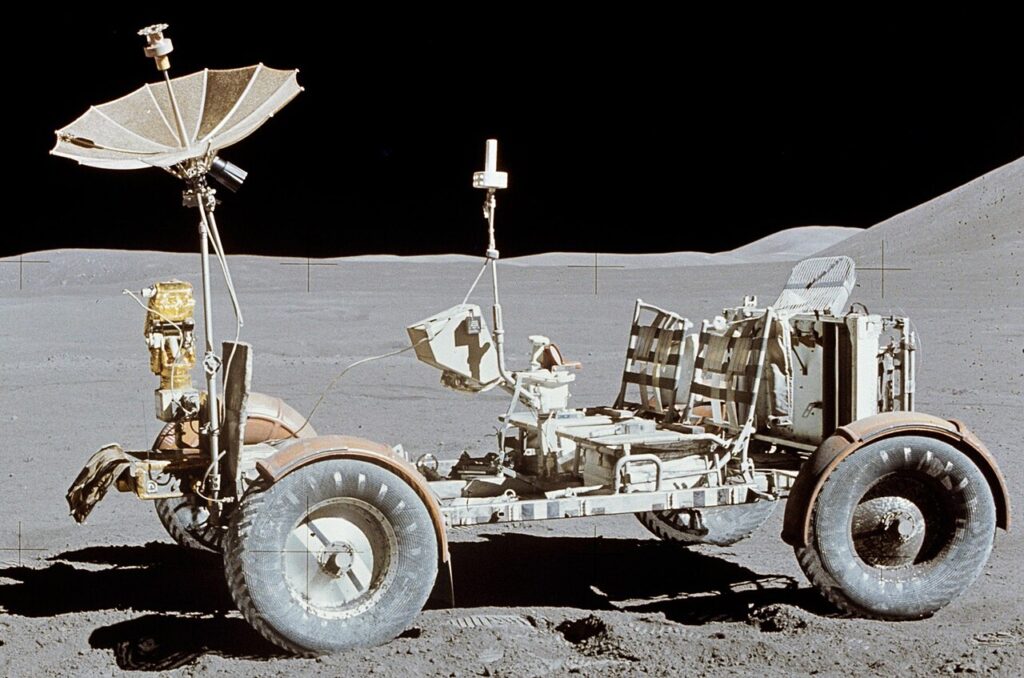
In 1971, the U.S. Apollo 15 mission used a battery-powered lunar rover, drawing global attention to electric vehicle technology and injecting new momentum into its development.
Modern Development: The Resurgence of Electric Vehicles
Since the 1990s, electric vehicles have entered their second golden age. With the maturation of lithium-ion battery technology, the performance of EVs has seen a qualitative leap. Lithium batteries offer high energy density, fast charging, and long lifespans, making electric vehicles suitable for most daily use needs.
In 1996, General Motors launched the EV1, the first mass-produced modern electric vehicle. Although the EV1 was eventually discontinued, it marked the beginning of a new chapter in modern electric vehicle development. Since then, major automakers have increased their investment in EV research and production, introducing a variety of electric vehicle models.
In the early 21st century, the founding of Tesla Inc. sparked a wave of electric vehicle development. Tesla’s advanced battery technology, intelligent driving systems, and stylish designs quickly gained global recognition and market share. The launch of models like the Model S and Model 3 not only changed traditional perceptions of electric vehicles but also drove the growth of the entire EV industry.
Advantages and Challenges of Electric Vehicles
Advantages:
- Environmental and Energy Efficiency: Electric vehicles produce no tailpipe emissions, effectively reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, which is crucial for improving environmental quality. Additionally, EVs are more energy-efficient, reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels.
- Quiet and Comfortable: Electric vehicles operate almost silently, providing a quieter and more comfortable experience for passengers.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Due to their simpler structure, lacking complex components like internal combustion engines and transmissions, electric vehicles generally have lower maintenance costs. Regular checks on batteries, tires, and brakes are typically all that’s needed.
Challenges:
- Range Anxiety: Despite advancements in battery technology, the limited range of electric vehicles remains a significant barrier to their widespread adoption. For users who frequently travel long distances, range anxiety is still a pressing issue.
- Inadequate Charging Infrastructure: The current charging infrastructure, such as charging stations, is still underdeveloped, especially in remote and rural areas. This limits the usability of electric vehicles.
- High Battery Costs: Batteries are the core component of electric vehicles and account for a significant portion of their cost. Although battery costs are gradually decreasing due to technological advancements and economies of scale, EVs are still more expensive than traditional gasoline-powered cars.
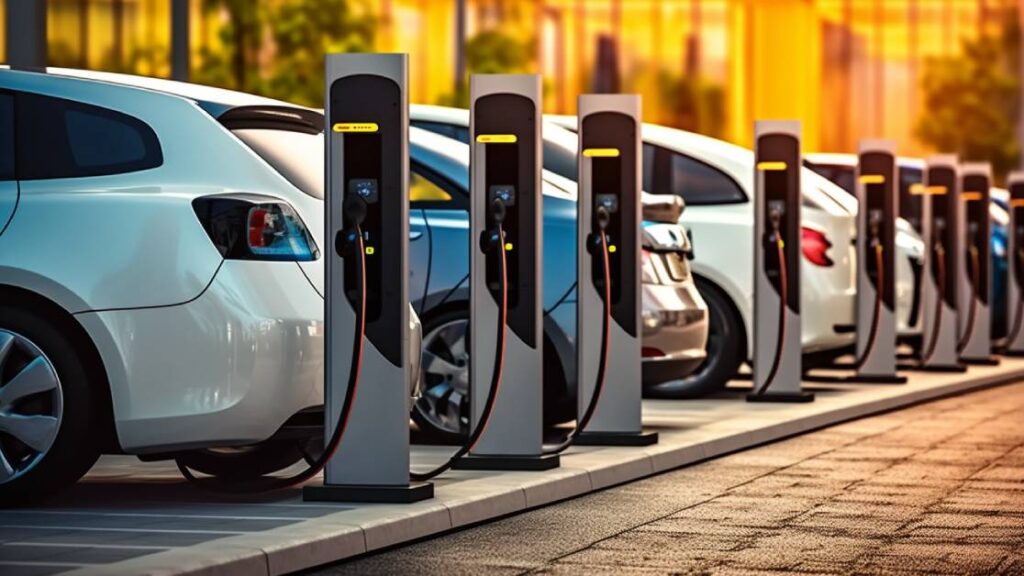

Electric Vehicle Price Trends
In recent years, as electric vehicle technology has matured and production scales have expanded, the prices of EVs have gradually declined. Government subsidies have further reduced the cost of purchasing electric vehicles for consumers.
However, prices vary significantly across different brands and models. Generally, small electric vehicles are more affordable, while mid-sized and luxury electric vehicles are more expensive. Factors such as battery capacity, range, and configurations also influence the price of electric vehicles.
Looking ahead, as battery technology continues to advance and charging infrastructure improves, the cost of electric vehicles is expected to decrease further, making them more accessible. By 2025, the price of electric vehicles is projected to be closer to that of traditional gasoline-powered cars, and their market share is expected to grow.
The Future of Electric Vehicles
From the creation of the first rudimentary electric vehicle to its current status as a global automotive industry hotspot, the history of electric vehicles has been filled with twists and triumphs. In the future, as technology continues to evolve and innovate, electric vehicles are expected to achieve breakthroughs in the following areas:
- Battery Technology Innovation: The development of higher energy density, faster-charging, and longer-lasting batteries, such as solid-state and hydrogen fuel cells, will further enhance the performance and competitiveness of electric vehicles.
- Integration of Autonomous Driving Technology: The fusion of autonomous driving technology with electric vehicles will enable features like self-driving and vehicle connectivity, offering users a more convenient and safe travel experience.
- Charging Infrastructure Development: Expanding charging infrastructure and improving the coverage and speed of charging stations will address users’ charging concerns.
- Market Popularization and Diversification: As prices decrease and performance improves, electric vehicles will become more widely adopted globally. At the same time, vehicle models will become more diverse, catering to different user needs.
The development of electric vehicles is not just about changing personal transportation; it also plays a crucial role in global energy restructuring and environmental protection. As a manufacturer of electric vehicle charging stations, we are deeply aware of our responsibility and mission in this historical process. We are committed to providing high-quality charging station products and services to global traders and users, working with partners to drive the growth of the electric vehicle industry and contribute to green transportation and a better future.
If you are interested in our charging station products, whether for trade cooperation or to learn more about our offerings, please contact us immediately. We look forward to opening a new chapter in the field of electric vehicle charging with you and witnessing the brilliance of the electric vehicle era together!

