Are you worried about elderly drivers struggling with complex charging station interfaces? It’s a valid concern, as technology sometimes moves faster than we can adapt.The good news is that charging station interfaces can be adapted for elderly users by focusing on simplicity, clarity, and accessibility. This includes larger fonts, simplified instructions, and easier cable handling.

But it’s not just about making things bigger. There’s a whole range of design considerations that can make a huge difference in the user experience for our senior citizens. Let’s dive into the specifics.
What Challenges Do the Elderly Face When Using Charging Pile Interfaces?
Imagine trying to learn a new, complex technology with vision changes, reduced dexterity, and perhaps some cognitive decline. This is reality.Elderly users often face challenges such as difficulty reading small text, understanding complex instructions, handling heavy cables, and navigating touch screen interfaces.
It is important to note that the problems that elderly drivers will encounter are not limited to interface usage. Other issues include:
Physical Limitations
- Reduced Dexterity and Strength: Many elderly individuals experience reduced hand strength and dexterity, making it difficult to manipulate small buttons, connect charging plugs, or handle heavy cables.
- Mobility Issues: Conditions like arthritis or limited mobility can make it challenging to reach charging ports, maneuver around the charging station, or stand for extended periods.
- Vision Impairment: Age-related vision changes, such as reduced visual acuity, sensitivity to glare, and difficulty seeing in low light, can make it hard to read displays, identify charging ports, and navigate the charging area.
Cognitive Challenges
- Memory and Processing Speed: Some elderly individuals may experience age-related cognitive decline, making it harder to remember charging procedures, process information quickly, or adapt to new technologies.
- Technology Anxiety: Seniors who are less familiar with technology may feel intimidated or overwhelmed by complex interfaces, touchscreens, or unfamiliar payment methods.
Environmental Factors
- Poor Lighting: Inadequate lighting at charging stations can exacerbate vision problems and make it difficult to locate and use the equipment safely.
- Weather Conditions: Extreme temperatures, rain, or snow can make it more challenging for elderly drivers to handle cables, operate touchscreens, or maintain balance while charging.
- Lack of Seating: The absence of nearby seating can be problematic for elderly users who may need to rest while waiting for their vehicle to charge.
How Can the Display of Charging Pile Screens Be Optimized to Be More Suitable for Elderly People to Read?
Think about your phone’s accessibility settings – bigger text, bolder fonts. We can apply the same principles here.Optimize charging pile screens for elderly users by using large, sans-serif fonts, high contrast color schemes (like black text on a white background), and adjustable brightness settings.
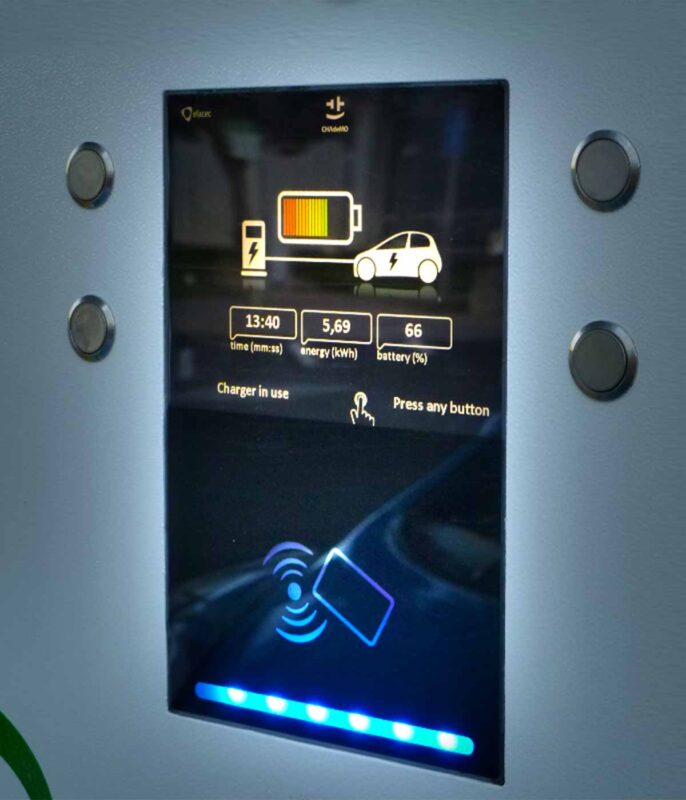
Font and Font Size
- Sans-Serif Fonts: Use clear, simple sans-serif fonts (like Arial, Helvetica, or Verdana) as they are generally easier to read than serif fonts (like Times New Roman).
- Large Font Size: The font size should be significantly larger than standard text. A minimum font size of 24 points is a good starting point, but larger may be necessary depending on the viewing distance.
- Bold Text: Using bold text can also help.
Contrast and Color
- High Contrast: Ensure a high contrast ratio between the text and the background. Black text on a white background or white text on a dark background generally provides the best readability.
- Avoid Problematic Colors: Avoid using color combinations that are difficult for people with color vision deficiencies to distinguish, such as red/green or blue/yellow.
Brightness and Glare
- Adjustable Brightness: Allow users to adjust the screen brightness to suit their individual needs and the ambient lighting conditions.
- Anti-Glare Coating: Use screens with an anti-glare coating to minimize reflections and improve visibility, especially in bright sunlight.
- Avoid Complex Graphics: Keep the display clean and uncluttered.
Can the Operation Process of Charging Piles Be Simplified to Reduce the Learning Cost for the Elderly?
Have you ever fumbled with a touchscreen with wet hands? Physical buttons offer tactile feedback that many seniors prefer.Simplify the operation process by using large, clearly labeled physical buttons for essential functions (like start/stop), and minimizing the reliance on complex touch screen menus.
Reasons to avoid using touchscreens
- Lack of Tactile Feedback: Touchscreens lack the physical feedback of buttons, making it difficult for users with reduced sensation or dexterity to know if they have successfully activated a control.
- Sensitivity Issues: Touchscreens can be overly sensitive or not sensitive enough, leading to accidental inputs or missed taps.
- Small Target Areas: Touchscreen interfaces often have small icons and buttons, which can be challenging for users with vision impairments or tremors to target accurately.
- Fingerprint Smudges: Smudges and fingerprints on the screen can reduce visibility and make it harder to read the display.
- Complexity of Gestures: Multi-touch gestures (like pinching or swiping) can be confusing and difficult for some elderly users to learn and remember.
Physical Buttons Strategy
- Essential Functions: Use physical buttons for core functions like starting and stopping the charging process, selecting charging levels, and initiating payment.
- Clear Labeling: Label each button with large, clear text and easily recognizable symbols.
- Tactile Feedback: Ensure buttons provide a distinct “click” or other tactile feedback when pressed.
- Spacing: Provide adequate spacing between buttons to prevent accidental presses.
- Illumination: Consider illuminating the buttons for better visibility in low-light conditions.
How Can the Design of Charging Guns and Cables Be Improved to Make Them Easier for the Elderly to Operate?
Imagine wrestling with a heavy, tangled cable – frustrating for anyone, but especially challenging for those with limited strength.Improve the design of charging guns and cables by using lightweight materials, providing sufficient cable length (but not excessive), and incorporating easy-to-use cable management systems.

Weight
- Lightweight Materials: Use lightweight materials for the charging gun and cable assembly, such as aluminum or high-strength plastics.
- Ergonomic Design: Design the charging gun with an ergonomic handle that is easy to grip and hold, even for users with arthritis or reduced hand strength.
Length
- Sufficient Length: Provide enough cable length to reach the charging port on various vehicle models without requiring excessive stretching or maneuvering.
- Avoid Excessive Length: However, avoid making the cable too long, as this can increase its weight and make it more difficult to manage. A length of 5 meters (about 16 feet) is often a good compromise.
Storage and Management
- Retractable Cables: Consider using retractable cable systems that automatically wind the cable back into the charging station after use.
- Cable Hooks or Reels: Provide clear and easy-to-use cable hooks or reels to keep the cable organized and prevent tangling.
- Cable Support: If the cable is particularly heavy, consider incorporating a cable support arm or mechanism to reduce the strain on the user.
- Motorized Cable Systems: Implement systems that minimize the need to handle heavy or unwieldy charging cables.
What Help Can Voice Prompts and Auxiliary Functions Provide to the Elderly?
Think of GPS voice guidance – a familiar and helpful technology that can be adapted for charging stations.Provide voice prompts and auxiliary functions like voice navigation through the charging process, and an easily accessible emergency call button for assistance.
Voice Prompts and Navigation
- Step-by-Step Guidance: Provide clear, concise voice prompts that guide the user through each step of the charging process, from plugging in the connector to initiating payment.
- Confirmation Messages: Use voice prompts to confirm actions, such as “Charging started” or “Payment successful.”
- Error Messages: Provide clear and informative voice messages if there is a problem, such as “Please check the connection” or “Payment failed.”
- Multilingual Support: Offer voice prompts in multiple languages to cater to a diverse user base.
Auxiliary Functions
- Emergency Call Button: Include a prominent, easily accessible emergency call button that connects the user to a help center or emergency services.
- Help Button: Provide a separate “Help” button that connects the user to a customer service representative who can provide assistance with the charging process.
- Remote Assistance: Consider incorporating remote assistance capabilities, allowing customer service representatives to remotely diagnose and troubleshoot charging issues.
How Can the Payment Methods of Charging Piles Be More in Line with the Habits of the Elderly?
Not everyone is comfortable with smartphone apps. Offering multiple payment options ensures inclusivity.Offer a variety of payment methods, including options familiar to the elderly like credit/debit card readers, and potentially even cash payment options where feasible.
Payment Method Considerations
- Contactless Payment: Offer contactless payment options, such as tap-to-pay with credit/debit cards or mobile wallets, as these are generally faster and easier to use than inserting cards.
- Chip Card Readers: Include traditional chip card readers for users who prefer to insert their cards.
- Avoid App-Only Payment: Do not rely solely on smartphone apps for payment, as some elderly users may not own smartphones or be comfortable using them for financial transactions.
- Cash is not practical for many reasons: Cash is not practical for many reasons, including concerns of vandalism.
User Interface for Payment
- Simple Steps: Minimize the number of steps required to complete a payment.
- Clear Instructions: Provide clear, concise instructions on the screen and/or through voice prompts.
- Large Buttons: Use large, clearly labeled buttons for selecting payment options and entering amounts.
- Confirmation Screens: Display confirmation screens to verify the payment amount and method before processing the transaction.
How Can Training and Guidance Help the Elderly Become Familiar with the Use of Charging Piles?
Think of the friendly assistance you might get at a new tech store – personalized support can make all the difference.
Offer training and guidance through on-site staff (where available), clear and simple instructional materials, and potentially even community outreach programs.
Training and Guidance Strategies
- On-Site Staff: If feasible, provide on-site staff at charging stations, especially during peak hours, to assist users with the charging process and answer questions.
- Clear Signage: Use clear, concise signage with large, easy-to-read text and graphics to explain the charging process.
- Instructional Videos: Create short, informative videos that demonstrate how to use the charging station. These videos can be displayed on the charging station screen or made available online.
- Simplified Manuals: If manuals are provided, they should be clear, concise, and use large print.
- Community Outreach: Partner with senior centers, community organizations, or driving schools to offer workshops or training sessions on electric vehicle charging.
- Face-to-Face instructions: Offer personalized training sessions to help elderly users become familiar with the charging process. Hands-on instruction is often more effective than manuals alone.
- Accessible Customer Service: Ensure customer service is available through various channels (phone, on-site assistance) and is trained to assist elderly users with specific needs.
What Are the Future Development Trends of Charging Pile Interfaces in Terms of Aging-Friendly Design?
We’re moving towards a future where technology adapts to us, not the other way around.Future trends point towards intelligent and personalized interfaces, potentially incorporating features like user profiles, AI-powered assistance, and even automated charging connections.

Intelligent Features
- User Profiles: Allow users to create profiles that store their preferences, such as preferred language, font size, and payment method. The charging station would then automatically adjust the interface based on the user’s profile.
- AI-Powered Assistance: Integrate AI-powered virtual assistants that can provide personalized guidance and support, answer questions, and troubleshoot problems.
- Predictive Assistance: Use machine learning to anticipate user needs and proactively offer assistance. For example, if the system detects that a user is having difficulty connecting the charging plug, it could automatically provide voice prompts or display helpful instructions.
Personalization
- Customizable Interfaces: Allow users to customize the appearance and layout of the interface, such as choosing different color schemes or button arrangements.
- Adaptive Learning: Design interfaces that adapt to the user’s behavior and skill level over time. For example, the system could gradually reduce the level of assistance provided as the user becomes more familiar with the charging process.
- Voice Control: Integrate voice control functionality to allow users to interact with the charging station using voice commands.
Conclusion
Adapting charging station interfaces for elderly users is not just about making things bigger or louder. It is about using thoughtful design to ensure the safety of elderly drivers. As a manufacturer specializing in customized production of electric vehicle charging products, TX can tailor the aforementioned features according to operators’ needs.By addressing these key areas, we can make EV charging accessible and user-friendly for everyone.

